India is synonymous with basmati rice, a long-grain aromatic rice variety cherished worldwide for its unique flavor, fragrance, and texture. In this blog, we explore the intricacies of basmati rice production in India, its significant contribution to the global rice market, and relevant statistics from recent years.
Basmati Rice Production in India
Cultivation Regions
Basmati rice is primarily cultivated in the northern regions of India, including:
- Punjab
- Haryana
- Uttar Pradesh
- Madhya Pradesh
- Himachal Pradesh
- Uttarakhand
- Jammu & Kashmir
These regions provide the ideal agro-climatic conditions for basmati rice, including fertile soil, specific weather patterns, and the pure water of Himalayan rivers.
Varieties of Basmati Rice
Several varieties of basmati rice are cultivated in India, each with distinct characteristics. Some of the popular varieties include:
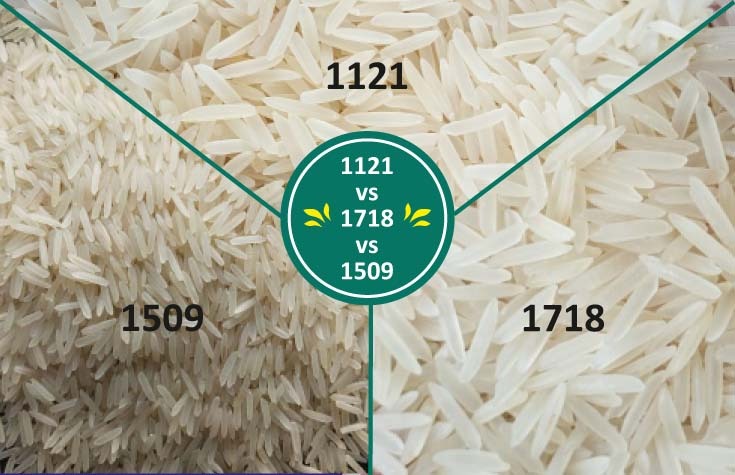
- Basmati 1121: Known for its extra-long grain and aromatic flavor.
- Basmati 1509: Appreciated for its short growth period and high yield.
- Pusa Basmati 1: A hybrid variety with superior grain quality and higher yield.
Agricultural Practices
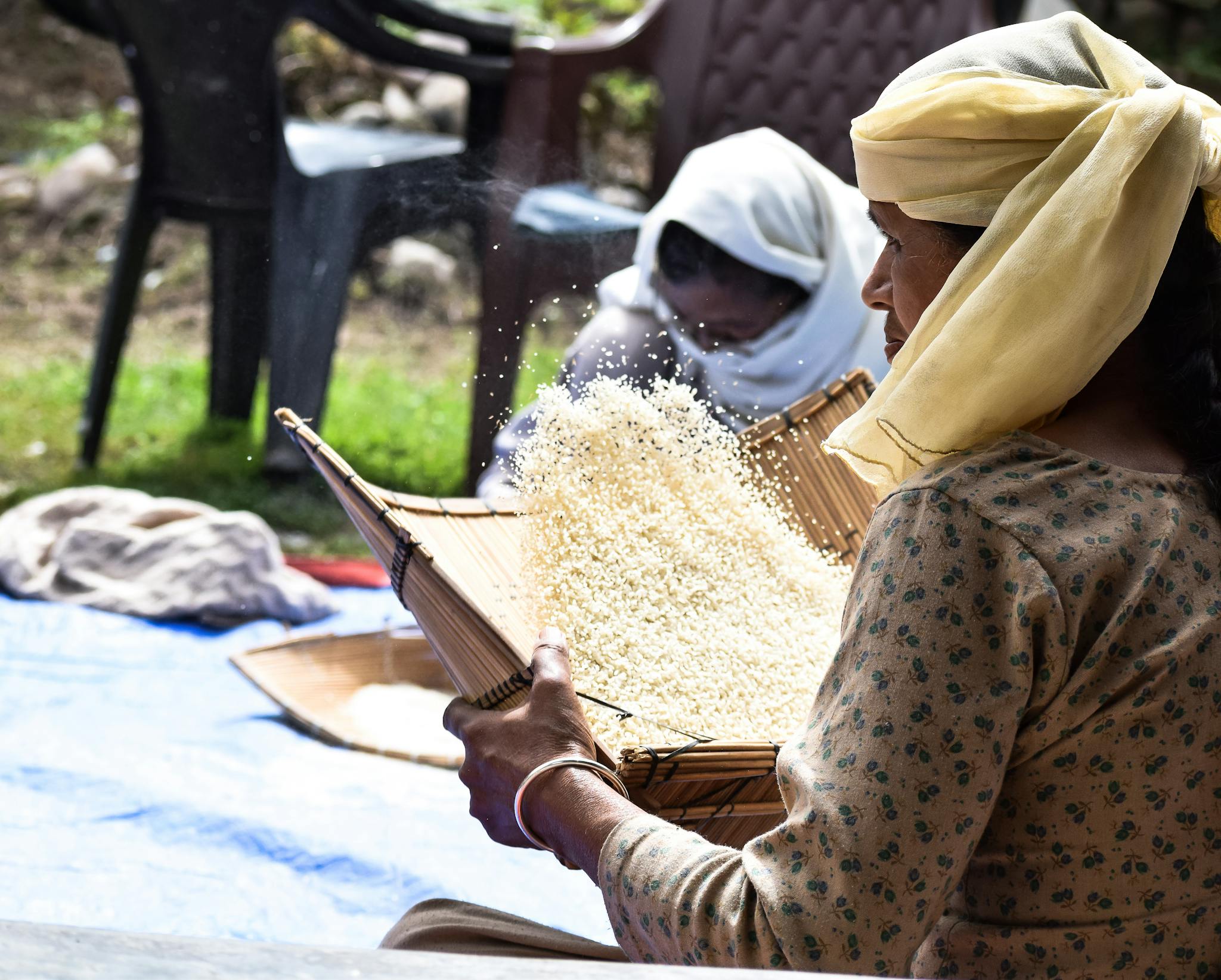
Indian farmers employ traditional and modern agricultural practices to cultivate basmati rice. The process involves:
- Sowing: Sowing seeds in nurseries before transplanting seedlings to paddy fields.
- Water Management: Implementing efficient irrigation practices to conserve water.
- Pest Management: Using integrated pest management techniques to reduce the use of chemical pesticides.
- Harvesting: Harvesting rice manually or with the help of machinery to ensure minimal grain breakage.
India’s Contribution to the Global Rice Market
India is a leading exporter of basmati rice, playing a pivotal role in the global rice market. The country’s high-quality basmati rice is in demand worldwide, particularly in the Middle East, Europe, and North America.
Export Statistics
India’s basmati rice exports have shown impressive growth over the years. Below are some key statistics:
- 2018-2019: India exported approximately 4.4 million metric tons of basmati rice, valued at around $4.7 billion.
- 2019-2020: Exports slightly decreased to 4.5 million metric tons, valued at $4.3 billion.
- 2020-2021: Despite the global pandemic, India exported 4.6 million metric tons of basmati rice, valued at $4.1 billion.
- 2021-2022: Exports rebounded, reaching around 4.2 million metric tons, valued at $4.4 billion.
Factors Contributing to India’s Success in the Basmati Market
- Quality and Standards: Indian basmati rice adheres to stringent quality standards, ensuring superior grain quality, aroma, and taste.
- Government Support: The Indian government provides support through various schemes and subsidies to encourage basmati rice cultivation and export.
- Innovative Farming Techniques: Adoption of modern agricultural practices and technology enhances yield and quality.
- Market Access: India has established strong trade relations with key importing countries, ensuring consistent demand.
Challenges and Future Prospects
While India remains a dominant player in the basmati rice market, several challenges need to be addressed:
Conclusion
- Climate Change: Unpredictable weather patterns can affect crop yield and quality.
- Water Scarcity: Efficient water management practices are essential to sustain basmati rice cultivation.
- Global Competition: Competing with other basmati rice-producing countries like Pakistan requires continuous improvement in quality and marketing strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is basmati rice? Basmati rice is a long-grain aromatic rice variety known for its unique flavor, fragrance, and texture. It is primarily grown in India, Pakistan, and Nepal.
2. Why is basmati rice so popular? Basmati rice is popular for its distinctive aroma, fluffy texture, and nutty flavor. It is a preferred choice for many traditional dishes in Indian, Middle Eastern, and Persian cuisines.
3. Is basmati rice gluten-free? Yes, basmati rice is naturally gluten-free, making it a suitable option for those with gluten intolerance or celiac disease.
4. Is basmati rice healthy? Basmati rice is a healthy option when consumed in moderation. It is low in fat, contains essential amino acids, and has a moderate glycemic index. Brown basmati rice offers more fiber and nutrients compared to white basmati rice.
5. How does basmati rice compare to jasmine rice? Basmati and jasmine rice are both long-grain varieties, but they differ in texture and aroma. Basmati rice has a nutty flavor and a fluffy, separate grain structure, while jasmine rice is more fragrant, with a slightly sticky texture when cooked.
6. Is basmati rice good for diabetics? Basmati rice, particularly brown basmati, has a lower glycemic index compared to other types of rice. This means it causes a slower, more gradual increase in blood sugar levels, making it a better option for people with diabetes.
7. Is basmati rice good for weight loss? Basmati rice can be part of a weight loss diet if consumed in moderation. Its lower glycemic index helps maintain stable blood sugar levels, which can reduce hunger and prevent overeating. Opting for brown basmati rice adds more fiber, aiding in digestion and keeping you fuller for longer.
8. What are the main regions in India where basmati rice is cultivated? Basmati rice is primarily cultivated in the northern regions of India, including Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, and Jammu & Kashmir.
9. What are the key varieties of basmati rice cultivated in India? Some popular varieties of basmati rice in India include Basmati 1121, Basmati 1509, and Pusa Basmati 1.
10. How much basmati rice does India export annually? India’s basmati rice exports have varied over the years. For instance, in 2018-2019, India exported approximately 4.4 million metric tons of basmati rice, valued at around $4.7 billion. In 2021-2022, exports were around 4.2 million metric tons, valued at $4.4 billion.
11. What are the main challenges faced by India’s basmati rice industry? Key challenges include climate change, water scarcity, and competition from other basmati rice-producing countries like Pakistan.
India’s basmati rice production is a cornerstone of the global rice market, contributing significantly to the country’s economy and agricultural landscape. With a combination of traditional practices, modern technology, and government support, India continues to maintain its leadership in basmati rice exports. As the world’s appetite for this aromatic rice grows, India’s commitment to quality and sustainability will ensure its prominent position in the global market for years to come.
For further information on basmati rice production and export trends, please visit the official websites of relevant agricultural and trade organizations.